The latitude and longitude coordinates of India are 20.5937° N, 78.9629° E.
What is latitude and longitude?
Latitude and longitude are a set of lines used to describe the location of any place on earth. The Earth is not a perfect sphere its polar radius and equatorial radius are not the same. There is bulging at the equator because of the earth’s rotation over its axis.
Therefore the shape of the earth is not a perfect sphere and it actually looks like an Oblate Spheroid. Because of its shape, there are difficulties in positioning its surface features and there is no point of reference from which to measure the relative positions of other points.
Therefore a set of lines is drawn on the map or globe to mark reference of the location of a different place on the earth’s surface. The basis of the geographical grid, formed by two natural points of reference is the North and South Pole.
The earth spins from west to east. The latitudes and longitudes are sets of horizontal and vertical lines.
The Horizontal lines are called Parallels of latitudes and Vertical lines are called the meridians of longitudes.
Longitudes
A set of vertical lines that join the North and South Poles are called the Meridians of Longitude. These lines converge at the poles and far apart at the equator.
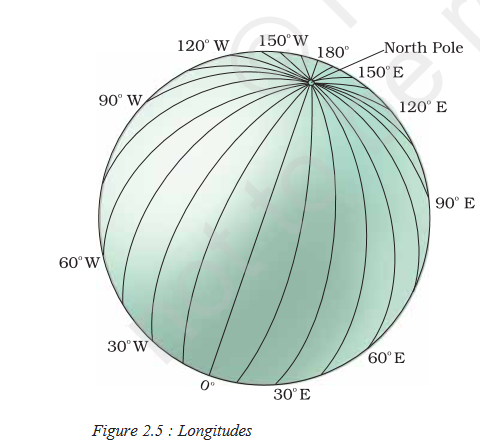
Longitudes of India
India’s longitudinal extent spans from 68°7’E to 97°25’E, covering a significant east-west distance. This longitudinal stretch has several implications for India.
This longitudinal stretch has several implications for India:
Time Zones
The large longitudinal extent could theoretically result in a time difference of up to 2 hours between the easternmost and westernmost points of the country. However, to maintain uniformity, India adheres to a single time zone, Indian Standard Time (IST), based on the 82.5° East longitude.
Sunrise and Sunset
Due to the longitudinal spread, the sun rises earlier in the eastern parts of India compared to the western regions. This variation in sunrise and sunset times influences daily routines and activities across the country.
Climate
The longitudinal extent can contribute to regional variations in climate, particularly in terms of monsoon patterns and temperature differences. The eastern and western coastal regions, for example, experience distinct climatic conditions due to their exposure to different ocean currents and wind systems.
Agricultural Seasons
The varying day lengths and solar radiation across different longitudes can impact the timing of agricultural seasons. Farmers in different regions may adopt different cropping patterns and irrigation practices to optimize their agricultural activities based on the local climatic conditions influenced by longitude.
Latitudes
These lines are drawn parallel to each other in an east-west direction and the Latitude at which the earth is divided into two halves is called the Equator. The equator is also called the Great Circle, as it is the largest circle and divides the globe into two halves.
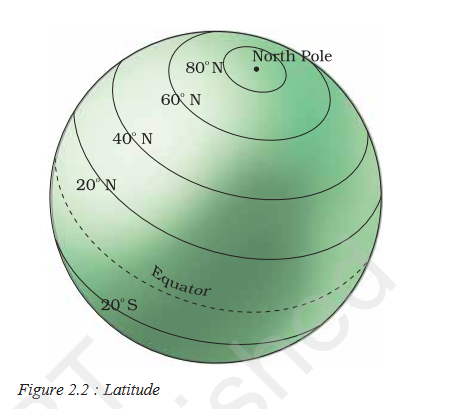
Other lines of latitudes are called Small Circle, as they are smaller than the Great Circle, and get smaller and smaller toward the poles and divide the earth into two unequal halves. All these lines of latitudes, including the Great Circle and Small Circle, are called parallels of latitude.
Latitudes of India
India’s latitudinal extent ranges from 8°4’N to 37°6’N. This means that the northernmost point of India lies at 37.6 degrees north of the equator, while the southernmost point is 8.4 degrees north.
This latitudinal extent has several implications for India:
Tropical Climate
The Tropic of Cancer, located at 23.5°N, passes through the middle of India. This contributes to the country’s predominantly tropical climate, characterized by hot and humid summers and mild winters.
Diverse Topography
India’s latitudinal extent results in a diverse range of landscapes, from the snow-capped Himalayas in the north to the tropical rainforests in the south.
Monsoon Patterns
The latitudinal position of India influences the country’s monsoon system. The seasonal reversal of winds brings rainfall to different parts of the country at different times.
Conclusion
The latitudes and longitudes are generally called Geographical coordinates because they provide a systematic network of the line by the which position of different surface characteristics of the Earth can be represented.
In the globe or map, an infinite number of Longitudes and latitudes can be drawn but only a selected number of lines are generally drawn. It is measured in degrees (°) as it represents Angular distances. Then each degree is further divided into 60 minutes ( ‘ ) and each minute into 60 seconds ( “ ).
Reference
- Globe latitude and longitude pdf
- https://ncert.nic.in/textbook/pdf/kegy303.pdf
- https://kids.britannica.com/kids/article/latitude-and-longitude/353366