Lower Palaeolithic Culture
During the lower Palaeolithic times, Upright man is believed to have lived in the Indian Subcontinent.
To add more strength to this theory, we found the first Palaeolithic tools in Pallavaram in Chennai, India, identified by Robert Bruce Foote in 1863, and then many Palaeolithic sites were discovered in India’s subcontinent.
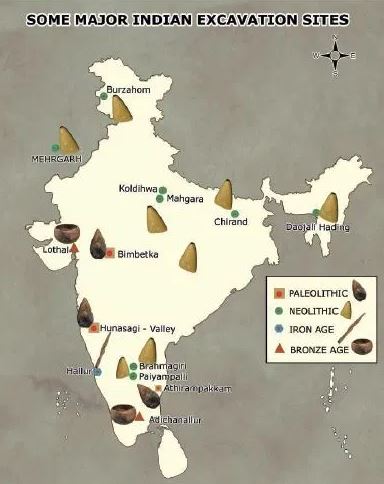
Lower Paleolithic sites in India
- Athirampakkam, Pallavaram (Tamil Nadu)
- Gudiyam, Hunsgi valley, Isampur (Karnataka)
- Bhimbetka (Madya Pradesh)
What are some Paleolithic tools?
The prehistoric study depends upon lithic tools.
Upright man-made enormous stone blocks, pebbles, and chipped tools out of other sturdy stones. Tools such as axes, cleavers, choppers are designed by flaking off the chips. They designed the tools which show the skill set of Prehuman. The tools were intended for hunting, butchering, skinning of animals, and processing food.
We divide the industries of Stone Age cultures into the early, middle, and late Acheulian industries. Early Acheulian tools include polyhedron, spheroids, hand axes, cleavers, and flake tools.
This tradition is absent in the Western Ghats, north-eastern India, and coastal areas, the reason might be Heavy rainfall in these areas and also lack of raw materials and Uncongenial conditions also prevented the occupation in the Western Ghats, north-eastern India, and coastal areas.
We find the Palaeolithic sites more in Central and in south-eastern India as these regions receive good rainfall, possess thick green cover, and are rich in resources. Some important areas where the Acheulian tools are found are Athirampakkam, Pallavaram, Gudiyam, Hunsgi valley, Isampur, and Bhimbetka.
Athirampakkam, Pallavaram (Tamil Nadu Formerly Madras, India) Hunsgi valley and Isampur(Karnataka, India) Bhimbetka (Madhya Pradesh, India)
Lower Paleolithic era
According to the latest research, the lower Palaeolithic began around two million years ago and this culture lasted up to 60,000 years ago.
Hominin and Animal Fossils of the Lower Palaeolithic
Hominin(ancestor of Humans) is rare in India and it is a very common fossil in Africa. The only known Hominin fossil of India is in Hathnora near Hoshangabad in Madhya Pradesh. The cranium is named Narmada human.
We found a partly preserved hominid skull cap in 1982 in a basal conglomerate deposit that represents Archaic Humans.
In Narmada valley, Elephas namadicus(Giant tusked Prehistoric elephant), Stegodon ganesa (a giant prehistoric elephant), Bos namadicus (wild cattle) and Equus namadicus (extinct great horse-like animal).
In Attirampakkam, Tamil Nadu –Teeth of Equus, evidence of water buffalo and nilgai and 17 animal hoof prints were found. These hoof prints suggest an open, wet landscape near the Chennai region during the prehistoric period.
The Way of Life of People in Lower Paleolithic
They fed on animals, nuts, fruits, and roots and lived in open-air, caves, valleys, and rock shelters as seen in Painting on the caves of Bhimbetka in Madhya Pradesh and Gudiyam near Chennai. The upright man had a complex language system like Humans, and they might have used sounds or few words or sign language.
They were intelligent enough to select stones as raw materials and use hammer stones to flake the rocks and design tools.
Middle Palaeolithic Culture
Lithic technology and species of humans diverged after 4,00,000 years BP (Before Present). Upright man existed in this period and they modernized middle Palaeolithic tools.
Around 3,00,000 years ago modern humans emerged. H.D. Sankalia identified the Middle Palaeolithic phase in India on the Pravara river at Nevasa. Several Middle Palaeolithic sites have been identified and recently Athirampakkam is identified which dates back to 3.85-1.72 lakh year B.P.
Indian Middle Palaeolithic and African Middle Palaeolithic cultures are probably of the same period.
Industries and Tool Types of Middle Palaeolithic
The Flake industry was the most in the Middle Palaeolithic period, and tools such as scrapers, borers, and points were made. For wood and skin, they used working scrappers.
The other tools of this period are hand axes, cleavers, choppers, chopping tools, projectile point, shouldered point, knives, etc.
Chronology of the Middle Palaeolithic
Middle palaeolithic is between 3,85,000 and 40,000 BCE. While we associate the European middle stone with Neanderthals, in Africa it is Humans. In India, there is we found no hominin fossils.
Distribution of the Middle Palaeolithic
Narmada, Godavari, Krishna, Yamuna, and other river valleys are some of the Middle Palaeolithic sites.
Life and Culture of the Middle Palaeolithic
The people lived in caves, rocks, and in the open air. They were hunters and gatherers. The tools became less and decreased the use of hand axes regarding other tools.
Stone tool preparation production using core preparation techniques. The raw materials used were chert, chalcedony, quartz, and jasper.
Upper Palaeolithic Culture
The phase that followed the Middle Palaeolithic phase is Upper Palaeolithic. The Upper Palaeolithic phase is marked by the increased cognitive capability of humans and tool technology innovations.
About 300,000 years ago, modern humans who first developed in sub-Saharan Africa migrated to various parts of Asia around 60,000 years ago. These populations from Africa replaced the previous population and handled the Upper Palaeolithic culture in India.
Lithic Tools and Industries
The lithic industry of the Upper Palaeolithic period is based on blade and bone tool Technologies. Microliths (tiny stone tools) were introduced in the Upper Palaeolithic Period and they made these tools using different varieties of silica-rich raw Materials.
We have found bone tools and faunal remains in Kurnool caves in Andhra Pradesh.
Chronology
The Upper Palaeolithic culture is represented in India at several sites. A time bracket of c. 40,000 years to 10,000 years BP is suggested For this period.
Distribution
Some Upper Palaeolithic sites are Meralbhavi, Kurnool caves, Godavarikhani, Baghor I and Baghor III, Patne, etc. We find evidence of microliths and Hominin fossils in Sri Lanka.
Incised ostrich eggshell, shell, stone beads are found in Jwalapuram in Andhra Pradesh, Patne and Batadomba-Lena, and Fa Hein caves in Sri Lanka. They had used ostrich eggshells as beads were found in Patne dated to 25,000 BP and Bhimbetka.
Ways of Life and Main Characteristics
Evidence of art in the Upper Palaeolithic period appears as paintings. We have also found beads and ornaments of this period.
The lithic blade industry advanced in this period. Some green color paintings of Bhimbetka are dated to the Upper Palaeolithic period based on style and archaeological evidence.
Conclusion
This article is written for the topic ‘Lower paleolithic sites in India’ for Upsc and other state service exams. This article discussed Paleolithic sites in India, their Chronology, characteristics, and their distribution.