International monetary fund’s Role and functions
The aim of the IMF(International Monetary Fund) is to promote economic and financial cooperation between its members. It is established to assist its member nation over the BOP(Balance of Payments) disequilibrium in a short time.
It has a currency of 189 members and the Republic of Nauru joined in 2016. IMF gold tranche – Gold Tranche or Reserve Tranche, represents a part of a member country’s quota with the IMF which exists in form of gold or foreign exchange.
For any member country, 25% of the total quota should be paid in the form of gold or foreign currency.
- To increase monetary cooperation between its member nations.
- Faster and balanced growth of trade internationally.
- Curbing the competitive exchange depreciation to ensure exchange rate stability.
- Ensuring smooth trade between its members by eliminating or reducing exchange controls.
- Promoting investment in developing countries by developed countries.
- To solve the international liquidity crisis.
Role of IMF in international liquidity
Imf offers borrowing facilities to its member nations to meet their deficits in Bop(Balance of Payments). Such borrowing facilities are useful when there is a problem with liquidity.
Assets may include Gold, Foreign exchange, etc.
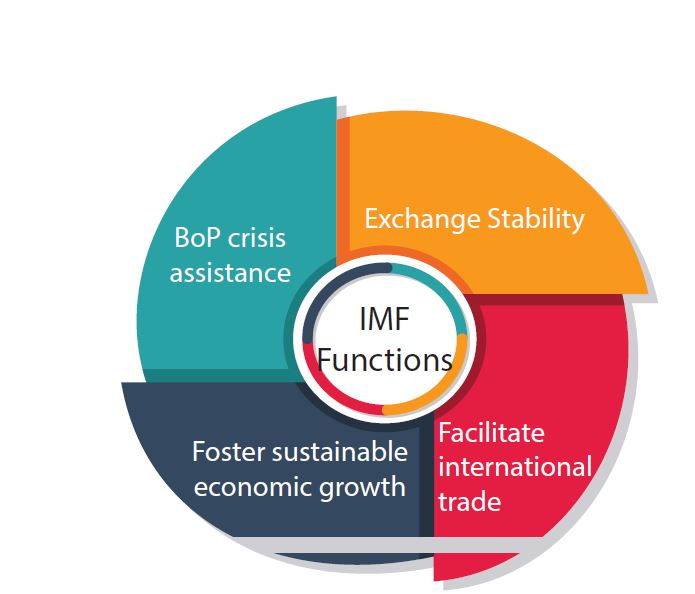
1. Stability in Exchange Rate
IMF is maintaining exchange rate stability. It emphasizes devaluation criteria.
It restricts its members to opt for multiple exchange rates. It also restricts its member to buy or sell gold at prices other than the declared par value.
2. Correcting BoP (Balance of Payments) Disequilibrium
International Monetary Fund helps countries in minimizing or eliminate the short period of BoP disequilibrium by lending or selling foreign currencies to the member nations.
3. Determining Par Value
International Monetary Fund determines the par value of the currencies of the member nations.
Every nation has to declare the par value of its currency in terms of the US Dollar or Gold, as per the articles of the Agreement of IMF.
By this Agreement, the IMF controls the international monetary system, in favour of some developed nations.
4. Balancing Demand and Supply of Currencies
International Monetary Fund’s import function is maintaining a balance between the demand and supply of different currencies.
It can declare a currency scarcely (Insufficient) that is in great demand.
It can increase scarce currency supply by getting it from a respected country or purchasing the same currency in exchange for gold.
Ex: If the Indian rupee has great demand in the international market, IMF either gets Indian Rupee from India or buys India Rupee in exchange for Gold.
5. Reducing Trade Restrictions
IMF also promotes reducing trade barriers such as reducing Tariffs ( Custom Duties/ Taxes) imposed by other member countries.
Also, aim to remove restrictions on the remittance of funds ( Funds coming from outside the country).
And also to avoid discriminating trade practices.
6. Providing Credit Facilities
IMF provides different lending and credit facilities to help its member countries.
It includes a basic credit facility for a period of 3 years, compensatory financing and a structural adjustment facility.
Other Functions of the International monetary fund
1. Financial
Balance of Payment assistance to short and medium-term.
2. Regulatory
Code of Conduct between its members
3. Consultative
Counselling and Technical consultancy.
International Monetary Fund offers Six Types of Facilities
1. Basic Credit Facility
IMF provides financial facilities such as assistance to the member when the country faces a Balance of Payments(Bop) by purchasing the fund in other currencies or Special Drawing Rights (SDR), which exchange its own currencies.
The loan is paid back to the members when the member repurchases its own currency or SDRs.
IMF allows its members to borrow unconditionally up to 25% of its quota it is called Reserve Tranche.
2. Extended Fund Facility
An additional borrowing facility of up to 140% of the regular member’s quota is given at a low-interest rate and limited up to a period of 3 years.
3. Compensatory Financing Facility
Compensatory financial assistance to the countries in which primary producing countries face a shortfall in export earnings. It was established in 1963. From 1981, the coverage was extended to the payment problem also.
This payment problem is caused due to cost fluctuations in cereal inputs.
Compensatory financing refers to international financial assistance to countries whose export earnings are impacted due to the decline in primary commodity prices. This system was instituted in 1963 by IMF.
This compensatory and contingency financing facility (CCFF), gives temporary finance to those countries that suffer from export receipts or temporary overrun in cereal import costs.
4. Buffer Stock Facility
It was started in 1969, the aim is to help agriculture-based countries with a financial contribution to buffer stock for the stabilization of prices of primary products.
buffer stock financing facility is designed to finance the member’s contribution to buffer stock arrangements in commodity agreements approved by the UN.
The Drawing under this method is permitted up to 50% of the Quota of the respective country.
5. Supplementary Financing Facility
The member countries suffer from payment problems due to the present quota size of borrowings etc, IMF provides supplementary financial assistance.
6. Structural Adjustment Facility
It was established in March 1986. Provides additional Balance of Payments (BoP) assistance on concessional terms to poorer members.
To assist low-income countries, In Dec 1987, Enhanced Structural Adjustment Facility (ESAF) was established.
The primary objective of SAF and ESAF is to force low-income members to make strong macroeconomic and structural programs to improve the balance of payment status and improve economic growth.
International Monetary Fund’s Achievements
1. Monetary Reserve Fund Establishment
The IMF funds are part of the sizeable stock of national currencies of different countries. IMF uses its stock to meet the foreign exchange requirements of its member nations.
2. Monetary discipline and Cooperation
IMF provides assistance only to those nations that take dedicated efforts to solve their problems.
3. Under Development Countries Problems
International Monetary Fund has taken many efforts and special interest by providing Financial assistance, overcoming BoP problems, etc.
In spite of all these efforts by the IMF, Under Developed countries continue to Under Developed, while developed countries develop more.
Relationship between India and IMF
India stood fifth in getting funds till 1970. India has good power to appoint the permanent Executive Director of the IMF.
India is one of the major beneficiaries of the IMF, in getting fund assistance. It is regularly paying its debt back to various agencies, and India is creditworthy.
India’s quota of Special Drawing Rights (SDR) is 5821.5 Million. India’s shareholding is 2.44% at the IMF, it is 3th largest.
Reports by IMF UPSC
- Global Financial Stability Report
- World Economic Outlook
Conclusion
IMF promotes international financial stability and monetary cooperation. It aimed to promote sustainable economic growth and reduce global poverty. IMF is governed by and is accountable to its 190 member nations.

